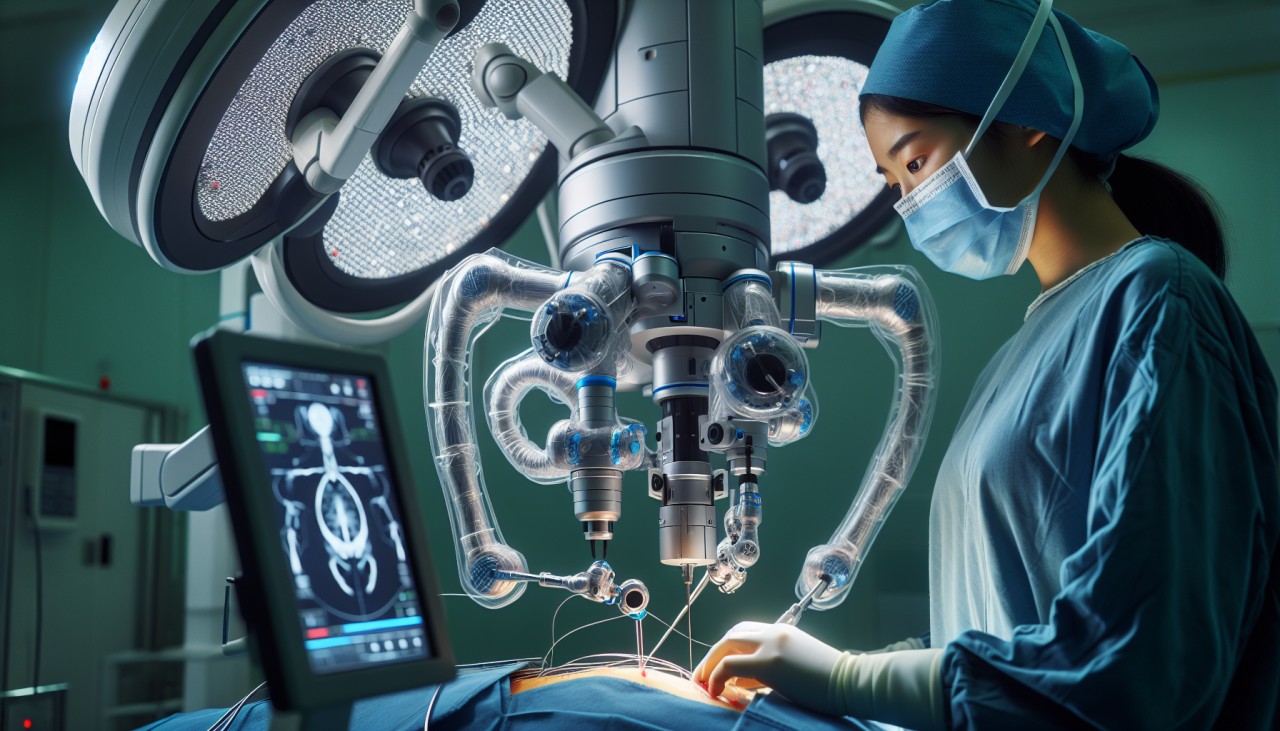
In recent years, the field of remote surgery has experienced remarkable advancements, fundamentally altering the landscape of healthcare delivery. This innovative approach allows surgeons to perform procedures on patients located thousands of miles away, effectively bridging the gap between medical expertise and patient needs. The concept of remote surgery, also known as telesurgery or cybersurgery, leverages cutting-edge technologies such as robotics, high-speed telecommunications, and real-time data transmission to facilitate surgical interventions across vast distances. The potential benefits of remote surgery are profound, particularly in addressing the disparities in access to specialized medical care. In many rural or underserved regions, patients often face significant challenges in obtaining timely and appropriate surgical treatments due to a shortage of qualified surgeons or advanced medical facilities. Remote surgery offers a viable solution by enabling experienced surgeons to extend their expertise beyond geographical constraints, ensuring that patients receive high-quality care regardless of their location. One of the most notable milestones in the evolution of remote surgery was the "Lindbergh operation" conducted in 2001. During this groundbreaking procedure, a team of French surgeons performed a cholecystectomy on a patient in Strasbourg, France, while operating from New York City, USA. This successful operation demonstrated the feasibility of conducting surgical procedures over long distances using advanced telecommunications and robotic systems. The success of the Lindbergh operation paved the way for further exploration and development in the field of remote surgery. Since then, numerous experiments and actual surgeries have been conducted, showcasing the potential of this technology to revolutionize healthcare delivery. For instance, in 2024, a team of Chinese doctors successfully performed a lung tumor removal surgery on a patient located 5,000 kilometers away, utilizing a 5G wireless connection. This achievement highlighted the significant progress in reducing latency and improving the reliability of remote surgical procedures. The integration of 5G technology has been a game-changer for remote surgery. The high-speed, low-latency communication provided by 5G networks addresses one of the critical challenges in telesurgery: the delay between the surgeon's commands and the robotic system's response. Minimizing this latency is essential to ensure the precision and safety of surgical interventions. The deployment of 5G networks has facilitated more reliable and efficient remote surgical procedures, making them more practical and accessible. Moreover, the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into remote surgical systems has further enhanced their capabilities. AI can assist in real-time data analysis, providing surgeons with critical insights and predictive analytics that inform decision-making during procedures. Additionally, AI-powered systems can monitor patient vitals and other parameters, alerting the surgical team to any anomalies that may require immediate attention. This integration of AI not only improves surgical outcomes but also contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of remote surgeries. The application of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies has also played a significant role in advancing remote surgery. Surgeons can now utilize VR simulations to plan and rehearse complex procedures, enhancing their preparedness and confidence. AR can overlay critical information onto the surgeon's field of view during surgery, providing real-time guidance and improving precision. These technologies have been particularly beneficial in training scenarios, allowing novice surgeons to practice and refine their skills in a risk-free environment. Despite the promising advancements, several challenges remain in the widespread adoption of remote surgery. Issues related to data security and patient privacy are paramount, as the transmission of sensitive medical information over networks introduces potential vulnerabilities. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and compliance with healthcare regulations is essential to maintain trust and integrity in remote surgical practices. Additionally, the high costs associated with setting up and maintaining remote surgical systems, including the purchase of robotic equipment and the establishment of secure communication networks, can be a significant barrier for healthcare institutions, especially in developing countries. Addressing these financial constraints through funding, subsidies, or cost-sharing models is crucial to make remote surgery a viable option for a broader range of healthcare providers. Furthermore, the need for standardized protocols and guidelines for remote surgical procedures is imperative to ensure consistency and quality of care. Establishing clear criteria for patient selection, surgical techniques, and post-operative care in the context of remote surgeries will help mitigate risks and enhance patient outcomes. Collaborative efforts among medical professionals, technologists, and policymakers are necessary to develop and implement these standards effectively. In conclusion, remote surgery represents a transformative advancement in the medical field, offering the potential to democratize access to specialized surgical care and improve health outcomes globally. While challenges persist, ongoing technological innovations and collaborative initiatives continue to drive progress, bringing the vision of accessible, high-quality surgical interventions to fruition for patients worldwide.
The rapid evolution of remote surgery has not only transformed the technical aspects of surgical procedures but has also had a profound impact on the global healthcare landscape. By enabling surgeons to operate on patients from distant locations, remote surgery has the potential to address longstanding issues related to healthcare accessibility, particularly in underserved and rural areas. The ability to provide specialized surgical care remotely ensures that patients, regardless of their geographic location, can benefit from the expertise of top-tier surgeons, thereby improving health outcomes and reducing disparities in healthcare delivery. One of the significant advantages of remote surgery is its capacity to facilitate continuous medical education and professional development for surgeons worldwide. Through telementoring and remote surgical assistance, experienced surgeons can guide and mentor less experienced colleagues in real-time, offering valuable insights and support during complex procedures. This collaborative approach not only enhances the skills and confidence of emerging surgeons but also fosters a global community of medical professionals committed to excellence in patient care. The integration of advanced technologies such as digital twins and augmented reality (AR) has further enhanced the capabilities of remote surgery. Digital twins, which are virtual replicas of physical entities, allow surgeons to simulate and plan surgical procedures with a high degree of accuracy, leading to improved outcomes. AR technologies provide real-time, context-specific information to surgeons during procedures, enhancing their situational awareness and precision. These innovations contribute to the overall safety and effectiveness of remote surgical interventions. The economic implications of remote surgery are multifaceted. On one hand, the initial investment in robotic systems and telecommunication infrastructure can be substantial. However, the long-term benefits, including reduced travel costs for patients, decreased hospital stays, and improved surgical outcomes, can offset these expenses. Moreover, the scalability of remote surgical services allows healthcare providers to extend their reach without the need for significant physical expansion, making it a cost-effective solution for delivering specialized care to a broader population. The success of remote surgery also hinges on the development and implementation of robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines. Establishing clear standards for patient consent, data privacy, and quality assurance is essential to maintain public trust and ensure the ethical practice of remote surgical procedures. Collaborative efforts among international health organizations, medical societies, and regulatory bodies are crucial in creating and enforcing these standards, promoting the safe and responsible adoption of remote surgery practices. In summary, remote surgery stands at the forefront of a healthcare revolution, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance the accessibility, quality, and efficiency of surgical care worldwide. While challenges persist, the ongoing advancements in technology, coupled with a collective commitment to innovation and collaboration, continue to drive the field forward, promising a future where specialized surgical expertise is within reach for all patients, regardless of their location.
Key Takeaways
- Remote surgery enables surgeons to perform procedures on patients located thousands of miles away.
- The integration of 5G technology has significantly reduced latency, enhancing the feasibility of remote surgeries.
- AI and machine learning algorithms assist in real-time data analysis, improving surgical decision-making.
- VR and AR technologies aid in surgical planning and training, enhancing precision and preparedness.
- Challenges such as data security, high costs, and the need for standardized protocols remain in the adoption of remote surgery.
- Remote surgery addresses healthcare accessibility issues in underserved and rural areas.
- Telementoring and remote surgical assistance facilitate continuous medical education and professional development.
- Digital twins and augmented reality enhance surgical planning and precision in remote procedures.
- The economic benefits of remote surgery include reduced patient travel costs and improved surgical outcomes.
- Robust regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines are essential for the safe and responsible adoption of remote surgery.